
Avamar System Overview
June 3, 2009Here is a overview I put together on an Avamar System, some of the functions held by the different types of nodes and examples of the 2 different types of nodes and backups.
Avamar Node Types and Processes
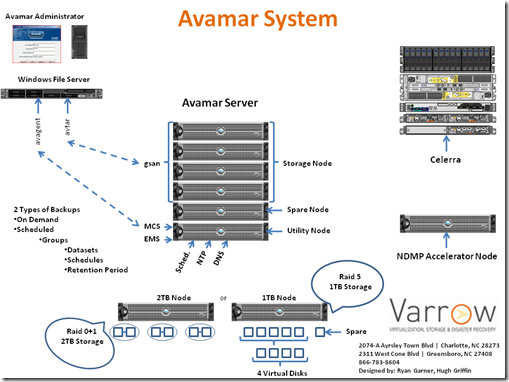
There are several different types of Nodes within an Avamar Server. The Utility node is the identity of the Avamar Server and provides the bulk of the internal Avamar server processes such as: Avamar Administrator (used to manage the Avamar Server from a gui), cron jobs, DNS, NTP, external authentication, web access, MCS and EMS.
MCS (Management Console Server) provides centralized management including scheduling of backups, restore of backups, monitoring and reporting.
EMS (Enterprise Manager Server) provides web based management for multiple Avamar Servers as well as monitoring and configuration for Avamar Replication.
Web Access provides access to documentation, backup plug-ins as well as remote File System restore access to end users.
Are next type of node is the Storage Node, which run a process called gsan. This service communicates with the avtar command on the individual backup clients. Avtar communicates with a storage nodes gsan process, then that storage node spreads the data across the available data nodes.
A Spare Node is an active node that is present in a multi-node RAIN (Redundant Array of Independent Nodes) grid. The interesting thing about the Spare Node is that it is NOT a hot spare. There is a procedure in place that needs to be followed when a failed Storage Node occurs. In fact, the Avamar Server doesn’t even care if the Spare Node is powered on, so if you are a “Green” conscience company, feel free to leave the Spare Node powered down. EMC Best Practice is to leave the Spare Node up and active though.
Avamar Backups clients can be installed with 2 different types of client plug-ins: File System and Databases. The Avamar client uses 2 processes in the backup and restore process: Avtar and Avagent. The Avagent process listens for backup/restore work orders from the MCS service on the Utility Node using port 28002 and executes the avtar command that handles the backup/restore processes and communicates with the gsan service on the storage nodes. This process is depicted in the included picture above.
Lastly, in a previous blog, I discussed the 2 different licensable options for Avamar and how the disks are comprised in each Storage Nodes type. These are depicted in the picture above as well as a breakdown of how the disks are structured.
Please stop back by later, I plan to talk about the NDMP Accelerator and it’s role in the Avamar System.


great information on the ndmp setup. however, i do have a few questions. during the add new system, it prompts for the network address or dns name of the celerra filer. your instructions said to input the ip of the data mover. i did and it could not ping it. how do you connect the ndmp to the network physically and setup the ips? there are four ports on the back, one connected to my avamar utility network and three more ports free.
You will need to create a network interface on the Celerra for the cge port plugged into the avamar utility network and make sure there is a route setup.
1. From the Network configuration page in Celerra Manager click the Interfaces tab.
2. Click New.
3. Choose appropriate Data Mover.
4. Enter the appropriate IP address, Name, Netmask, and Broadcast Address that is on the same network as the Avamar Utility Node. Click OK.
From the Network Configuration page, there should be a tab for Ping, from there try and ping the IP address of the Avamar Utility Node
When running the NDMP setup, you will want to use the IP address of the network interface you created for the cge port that is on the same network as the Avamar Utility Node.
Let me know if you have other questions.
Are there any independent training resources that I can pick up on Amazon?